Charts
Bar charts
Default
Bar charts use vertical or horizontal data markers to compare individual values; You can use it to compare discrete data or show trends over time.
Grouped bar
A grouped bar chart, also known as clustered bar graph, multi-set bar chart, or grouped column chart, is a type of bar graph that is used to compare values across multiple categories.
Stacked bar
Stacked bar charts are useful for comparing proportional contributions within a category. They plot the relative value that each data series contributes to the total.
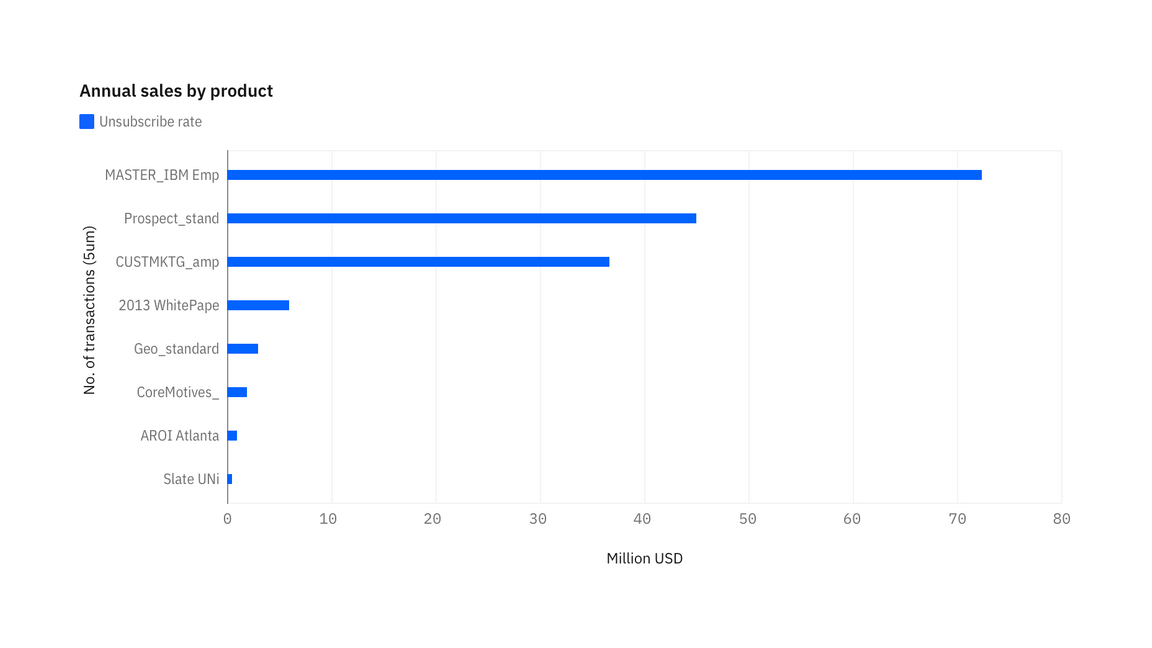
Horizontal bar
The horizontal bar chart follows the same principles as a vertical column chart only the x- and y-axis are switched.
Note: this chart is currently a concept and not included in the Carbon Charts repository yet. For more information, please go to the Carbon-charts GitHub repository.
Line Chart
Default
Line charts plot data at regular points connected by lines. You can use line visualizations to show trends over time and compare many data series.
Step line chart
Step line chart plot data at regular points, forming a series of steps between data points. You can use line visualizations to show trends over time and compare many data series.
Middle
Before
After (regular)
Curved line chart
Natural curve
Bundle curve
Monotone Y Curve
Monotone X Curve
Area chart
Defautl
Area charts are like line charts, but the areas below the lines are filled with colors or patterns. Stacked charts are useful for comparing proportional contributions within a category. They plot the relative value that each data series contributes to the total.
Stacked area chart
Stacked are charts are useful for comparing proportional contributions within a category. They plot the relative value that each data series contributes to the total.
Note: this chart is currently a Work In Progress. To see our roadmap, request missing guidance, or contribute your own content, please go to Carbon-charts GitHub repository.
Polar charts
Pie
Donut
Scatterplot
Default
Scatter visualizations use data points to plot two measures anywhere along a scale, not only at regular tick marks. You can use scatter visualizations to explore correlations between different measures.
Bubble chart
Bubble charts use data points and bubbles to plot measures anywhere along a scale. One measure is plotted along each axis. The size of the bubble represents a third measure. You can use bubble charts to represent financial data or any data where measure values are related.
Meter and gauge
Meter and gauge are useful for showing values between a small number of variables either by using multiple markers on the same meter or gauge, or by using multiples of the chart.
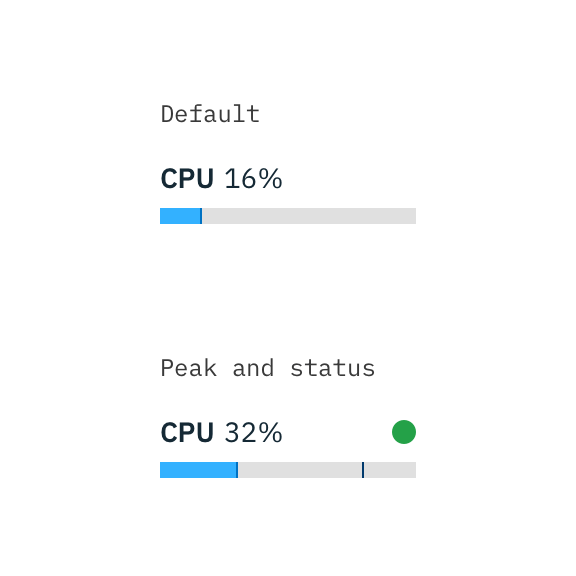
Meter can represent data with a current value, min and maximum, and peak or averages.
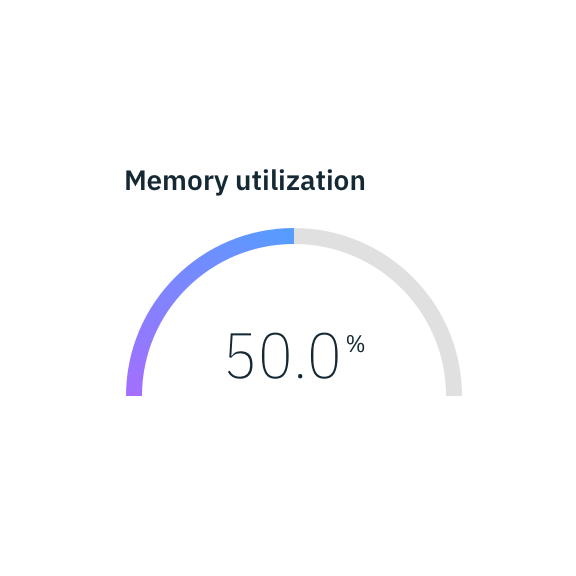
Gauge animates to the current value when dashboard loads to create emphasis.